When Inputs Bite Back: Cost Curves Rewrite Industry
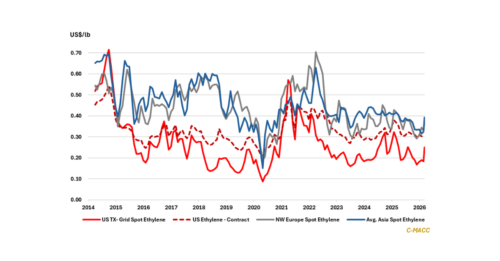
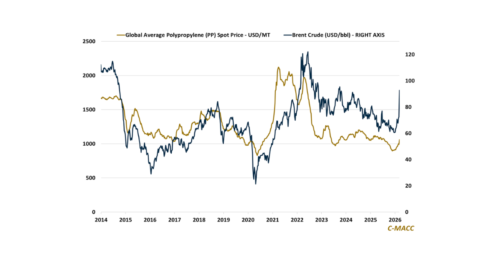
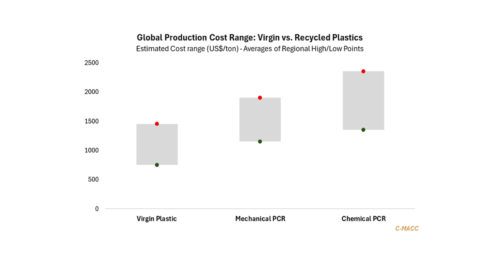
1st Topic of the Week: Energy-driven resin repricing narrows virgin-PCR gaps, benefiting circular adoption and shifting advantage toward suppliers that control feedstock, specification, and customer